A well-designed curriculum is the foundation of a successful education system. Curriculum development involves creating structured learning experiences that align with educational goals, meet student needs, and prepare learners for future challenges. A well-structured curriculum fosters critical thinking, creativity, and lifelong learning. This article explores the key principles, steps, and strategies involved in building educational programs that foster success.
Understanding Curriculum Development

Curriculum development is the process of designing, organizing, and refining educational programs. It involves selecting learning objectives, teaching methods, assessments, and instructional materials that align with academic standards and societal needs.
Types of Curriculum
- Formal Curriculum – Structured programs designed by educational institutions, including lesson plans and standardized courses.
- Hidden Curriculum – Unwritten, informal lessons students learn through school culture and teacher expectations.
- Core Curriculum – Essential subjects such as math, science, language arts, and social studies.
- Elective Curriculum – Optional subjects that allow students to explore personal interests, such as arts, music, and technology.
- Integrated Curriculum – Interdisciplinary approach that combines multiple subjects into meaningful learning experiences.
Key Principles of Curriculum Development
For a curriculum to be effective, it must follow certain principles:
1. Alignment with Educational Standards
Curricula should align with national and international educational standards to ensure consistency and relevance.
2. Student-Centered Learning
A successful curriculum focuses on the needs, interests, and learning styles of students rather than just delivering content.
3. Flexibility and Adaptability
A well-designed curriculum allows for modifications based on student progress, technological advancements, and societal changes.
4. Inclusivity and Diversity
The curriculum should accommodate diverse learning needs, cultural backgrounds, and abilities, ensuring equal access to education.
5. Balance Between Theory and Practice
A strong curriculum integrates both conceptual knowledge and practical applications to enhance student engagement and real-world problem-solving skills.
6. Assessment and Continuous Improvement
Regular evaluations ensure that the curriculum remains effective and relevant in achieving learning goals.
Steps in Curriculum Development
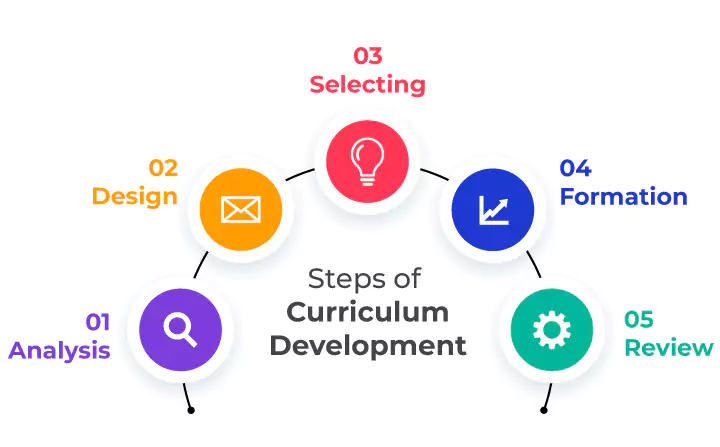
1. Needs Assessment and Goal Setting
Before designing a curriculum, it is essential to understand the needs of students, educators, and society. Key steps include:
- Identifying learning gaps.
- Conducting surveys and research on student interests and industry demands.
- Setting clear, measurable learning objectives.
2. Designing Learning Outcomes
Learning outcomes define what students should achieve at the end of a course or program. They should be:
- Specific – Clearly outline what students will learn.
- Measurable – Allow assessment of student progress.
- Achievable – Realistic for students to accomplish.
- Relevant – Align with real-world applications.
- Time-Bound – Set within a specific timeframe.
3. Selecting Instructional Strategies
Effective teaching methods enhance student engagement and understanding. Strategies include:
- Active Learning – Encourages hands-on activities and problem-solving.
- Blended Learning – Combines in-person and digital learning experiences.
- Inquiry-Based Learning – Promotes curiosity and critical thinking.
- Collaborative Learning – Encourages teamwork and peer interaction.
- Project-Based Learning (PBL) – Allows students to work on real-world problems.
4. Developing Course Content and Materials
Curriculum content should align with learning outcomes and use diverse instructional materials such as:
- Textbooks and Articles – Traditional learning resources.
- Videos and Multimedia – Engaging digital content for visual learners.
- Interactive Simulations – Hands-on virtual learning experiences.
- Case Studies and Real-Life Examples – Practical applications of theoretical concepts.
5. Assessment and Evaluation Methods
Assessments measure student learning and curriculum effectiveness. Types of assessments include:
- Formative Assessment – Ongoing evaluations like quizzes and class discussions.
- Summative Assessment – Final exams, projects, and standardized tests.
- Authentic Assessment – Performance-based tasks, portfolios, and real-world applications.
- Self and Peer Assessment – Encourages students to reflect on their progress.
6. Implementation and Teacher Training
Educators must be equipped with the knowledge and skills to effectively deliver the curriculum. Schools should:
- Conduct professional development workshops.
- Provide teaching resources and digital tools.
- Encourage collaboration among teachers to refine instructional strategies.
7. Continuous Review and Improvement
A curriculum should evolve with changing educational needs and technological advancements. Regular feedback from students, teachers, and stakeholders ensures its effectiveness.
Challenges in Curriculum Development and Solutions
1. Keeping Up with Technological Changes
- Solution: Integrate digital tools, e-learning platforms, and artificial intelligence into the curriculum.
2. Addressing Diverse Learning Needs
- Solution: Use differentiated instruction and personalized learning plans.
3. Balancing Rigid Standards with Flexibility
- Solution: Maintain core requirements while allowing room for innovative teaching methods.
4. Resource Constraints
- Solution: Leverage open educational resources (OERs) and community partnerships to support curriculum implementation.
Best Practices for Developing an Effective Curriculum
- Engage Stakeholders – Involve educators, students, parents, and industry professionals in the development process.
- Foster Critical Thinking and Creativity – Design activities that encourage problem-solving and innovation.
- Integrate Real-World Applications – Align learning with industry trends and practical skills.
- Encourage Interdisciplinary Learning – Combine subjects for a holistic learning experience.
- Promote Lifelong Learning Skills – Focus on adaptability, collaboration, and digital literacy.
Conclusion
Curriculum development is a dynamic process that requires careful planning, innovation, and continuous improvement. By creating educational programs that align with learning objectives, student needs, and real-world demands, educators can foster academic success and lifelong learning. A well-structured curriculum not only prepares students for careers but also equips them with the critical thinking and problem-solving skills necessary to navigate an ever-changing world.