Pedagogy refers to the method and practice of teaching. It is both an art and a science—blending creative instructional techniques with evidence-based strategies to promote meaningful learning. Whether you’re a classroom teacher, a university lecturer, or a training professional, understanding pedagogy is essential for creating effective and engaging educational experiences.
In this article, we’ll explore what pedagogy means, key approaches to teaching, and how pedagogy shapes student success in both traditional and modern learning environments.
🎓 What Is Pedagogy?
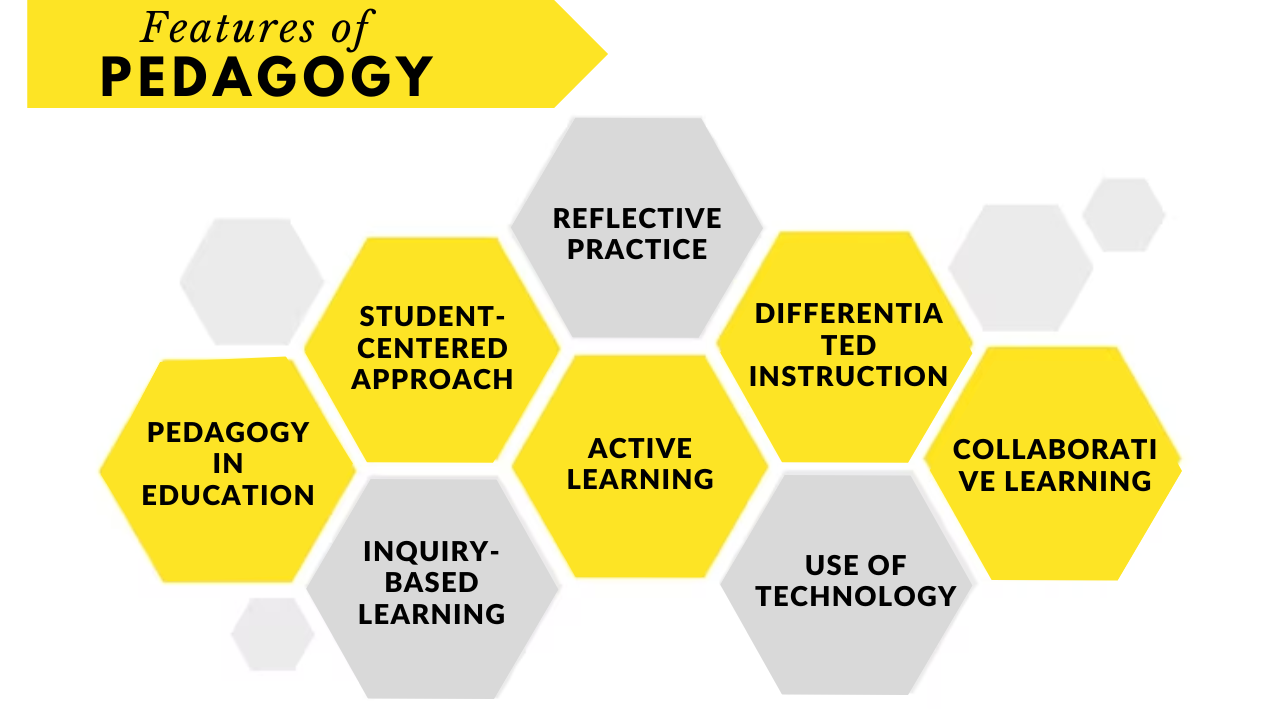
At its core, pedagogy is the theory and practice of how teaching is conducted. It encompasses everything from the way lessons are delivered, to the structure of classroom activities, to how student understanding is assessed. Pedagogy goes beyond simply delivering content—it aims to inspire curiosity, promote critical thinking, and support different learning styles.
🧠 The Dual Nature: Pedagogy as Art and Science
✅ As an Art
-
Requires creativity, adaptability, and intuition
-
Involves building relationships with students
-
Emphasizes tone, empathy, engagement, and cultural relevance
✅ As a Science
-
Based on research, cognitive psychology, and instructional theory
-
Uses data and feedback to improve outcomes
-
Relies on structured methodologies and measurable goals
Great teachers often blend both sides—drawing on proven strategies while tailoring them to the unique dynamics of their classroom.
📚 Key Pedagogical Theories and Approaches
Understanding different pedagogical models helps educators choose the best method for their learners. Here are a few foundational theories knowledge:
🧒 Constructivism (Jean Piaget, Lev Vygotsky)
-
Learners build knowledge through experiences
-
Emphasizes discovery learning and student engagement
🧩 Behaviorism (B.F. Skinner, John Watson)
-
Learning is shaped by responses to stimuli
-
Reinforcement and repetition play key roles
🌐 Social Learning (Albert Bandura)
-
Learning happens through observation and imitation
-
Highlights modeling and the importance of social context
🧑🏫 Humanism (Carl Rogers)
-
Focuses on the whole learner—emotionally and intellectually
-
Prioritizes student-centered and supportive environments
🔄 Cognitivism
-
Views learning as an internal mental process
-
Encourages strategies like chunking, scaffolding, and metacognition
🏫 Types of Pedagogical Approaches
Depending on the goals, learners, and context, different styles of teaching may be used:
| Approach | Description |
|---|---|
| Direct Instruction | Teacher-led lessons with clear objectives and structure |
| Inquiry-Based Learning | Students explore questions and problems to construct understanding |
| Project-Based Learning | Real-world tasks encourage collaboration and deep learning |
| Flipped Classroom | Students learn content at home and apply it in class |
| Differentiated Instruction | Tailored methods to meet diverse learner needs |
🧰 Elements of Effective Pedagogy
Great pedagogy involves more than just knowledge transfer. Key components include:
-
Lesson Planning: Clear objectives, structured content, and purposeful activities
-
Assessment: Formative (ongoing) and summative (final) assessments to guide learning
-
Classroom Management: Creating a safe and respectful learning environment
-
Student Engagement: Encouraging participation and motivation
-
Reflection and Adaptation: Using feedback and reflection to improve teaching
🌍 Pedagogy in a Modern Context
The rise of online learning, technology integration, and global classrooms has reshaped pedagogy:
-
EdTech Tools: Smartboards, learning apps, and digital platforms enhance interactivity
-
Remote Learning: Requires new strategies for student engagement and accountability
-
Inclusive Pedagogy: Acknowledges diverse backgrounds, learning needs, and accessibility
-
Culturally Responsive Teaching: Connects curriculum to students’ cultural contexts
💡 Why Pedagogy Matters
Understanding pedagogy empowers educators to:
-
Support diverse learners effectively
-
Improve student outcomes and retention
-
Make teaching more intentional and reflective
-
Foster lifelong learning skills in students
-
Stay current with best practices in education
Whether teaching children or adults, the right pedagogical approach makes the difference between passive instruction and active, meaningful learning.
🏁 Conclusion: Teaching with Purpose
Pedagogy is at the heart of every educational experience. It blends knowledge, empathy, structure, and innovation to help learners thrive. As education continues to evolve, embracing strong pedagogical principles ensures that teaching remains relevant, inclusive, and impactful.
📚 Great pedagogy doesn’t just teach facts—it transforms minds.
Enhance your web design with unique CSS snippets! Explore CSS Mayo for stylish, modern coding solutions. – https://www.cssmayo.com

